Amoxicillin
-
-
Amoxicillin 500mg | Milpharm – (21 Tablets)
£29.99Original price was: £29.99.£14.99Current price is: £14.99. -
Amoxicillin 500mg | Rudipharm – (21 Capsules)
£29.99Original price was: £29.99.£14.99Current price is: £14.99. -
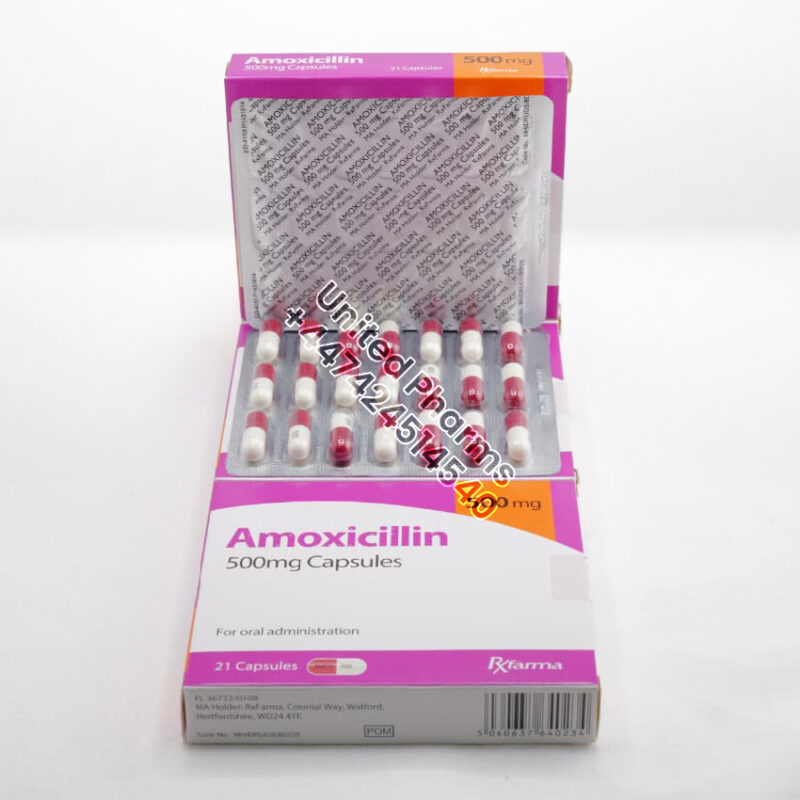

Amoxicillin 500mg | RXfarma – (21 Capsules)
£29.99Original price was: £29.99.£14.99Current price is: £14.99.
End of content
End of content
Gabapentin – Buy in UK/EU
Gabapentin is a prescription-only medicine widely used in the UK and EU for the treatment of neuropathic pain, epilepsy, and sometimes restless legs syndrome (RLS). Originally developed as an anticonvulsant, it has become a first-line therapy for nerve-related pain conditions due to its ability to calm overactive nerve signalling in the brain and spinal cord.
In the UK and EU, Gabapentin is available under multiple trusted pharmaceutical brands, offering patients consistent quality and bioequivalence regardless of manufacturer.
UK & EU Brand Names of Gabapentin
Common licensed brands include:
Neurontin (Pfizer – original branded formulation)
Aurobindo Gabapentin
Actavis Gabapentin
Teva Gabapentin
Winthrop Gabapentin (Sanofi)
Mylan Gabapentin
Crescent Pharma Gabapentin
Milpharm Gabapentin
Tillomed Gabapentin
Sandoz Gabapentin
Dr Reddy’s Gabapentin
All approved generic versions meet MHRA (UK) and EMA (EU) regulatory standards for quality, strength, and safety.
What Gabapentin Is Used For
1. Neuropathic Pain
Gabapentin is commonly prescribed for nerve-related pain caused by:
Diabetes (diabetic neuropathy)
Shingles (post-herpetic neuralgia)
Nerve injury
Spinal disc problems
Peripheral neuropathy
2. Epilepsy
Used alongside other medicines to help prevent partial seizures in adults and children.
3. Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS)
Some EU regions prescribe Gabapentin for RLS when first-line treatments are unsuitable.
How Gabapentin Works (Simple Explanation)
Gabapentin binds to specific calcium channels in the nervous system, reducing abnormal electrical activity and lowering the release of pain-signalling neurotransmitters.
This helps stabilise nerve activity, reducing pain, tingling, burning, and seizure frequency.
Advantages of Gabapentin
 Effective for Chronic Nerve Pain
Effective for Chronic Nerve Pain
Often helps when traditional painkillers (paracetamol, NSAIDs) fail.
 Non-addictive in most patients
Non-addictive in most patients
Though misuse exists, it is not an opioid and has a lower dependency risk compared to other pain medicines.
 Widely Available & Cost-Effective
Widely Available & Cost-Effective
Strong generic availability across UK/EU lowers cost and increases accessibility.
 Suitable for Long-Term Management
Suitable for Long-Term Management
Prescribers often use it safely for ongoing nerve pain or seizure control.
 Minimal interactions with many medications
Minimal interactions with many medications
Generally well-tolerated alongside antidepressants, painkillers, or antiepileptics.
Disadvantages of Gabapentin
✘ Drowsiness & dizziness
Common during early treatment or dose increases.
✘ Possible weight gain or swelling
Fluid retention and appetite changes may occur in some patients.
✘ Withdrawal symptoms if stopped suddenly
Including anxiety, sweating, and rebound pain.
✘ May take time to work
Can require weeks of dose titration for full effect.
✘ Potential misuse in high doses
Now a Schedule 3 controlled drug in the UK (since 2019) due to misuse cases.
When NOT to Use Gabapentin
Avoid or use only under medical supervision if:
You have severe kidney disease (dose adjustments required).
You are allergic to Gabapentin or any capsule ingredients.
You are pregnant or breastfeeding (risk–benefit must be assessed).
You have a history of substance misuse (requires careful monitoring).
You operate heavy machinery or drive (Gabapentin can impair reaction time).
You suddenly stop taking it – withdrawal symptoms may occur.
Key Symptoms Gabapentin Helps With
Burning or stabbing nerve pain
Tingling or “pins and needles” sensations
Shooting pain down legs or arms
Shingles-related nerve pain
Electric-shock sensations
Seizures (when used for epilepsy)
Night-time leg discomfort (RLS)
FAQ: Gabapentin (UK & EU)
1. Is Gabapentin a painkiller?
Not in the traditional sense. It is a neuropathic pain modulator, effective specifically for nerve pain.
2. How long does Gabapentin take to work?
Most people notice improvement within 1–2 weeks, but full benefits can take up to 6 weeks, depending on the dose.
3. What is the usual dosage?
Common doses range from 300mg to 3600mg per day, split into 3 doses. Your prescriber determines the correct schedule.
4. Can I drink alcohol on Gabapentin?
Alcohol increases drowsiness and dizziness, so it should be limited or avoided.
5. Is Gabapentin addictive?
While not classically addictive, misuse is possible, especially at very high doses. It is controlled in the UK for this reason.
6. Can Gabapentin be taken with antidepressants?
Often yes. Many UK/EU doctors combine it with SSRIs, SNRIs, or amitriptyline for difficult nerve pain.
7. Does Gabapentin affect sleep?
It may improve sleep in those with nerve pain but cause daytime drowsiness in some users.
Conclusion
Gabapentin remains one of the most widely prescribed and effective treatments for neuropathic pain and epilepsy across the UK and EU. With strong clinical backing, broad brand availability, and a well-understood safety profile, it is a reliable option for patients who struggle with chronic nerve-related pain.
However, like all medicines, it must be used responsibly under medical guidance—especially due to its sedative effects, tapering requirements, and controlled-status regulations in the UK.
When taken correctly, Gabapentin offers substantial and lasting relief, restoring comfort and improving quality of life for many patients.

 Effective for Chronic Nerve Pain
Effective for Chronic Nerve Pain